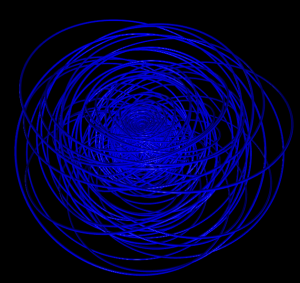
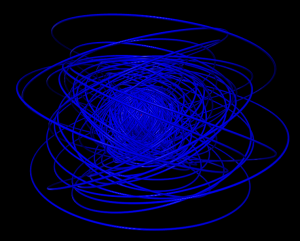
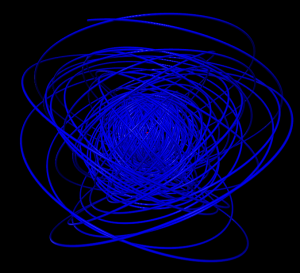
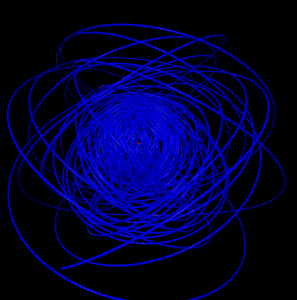
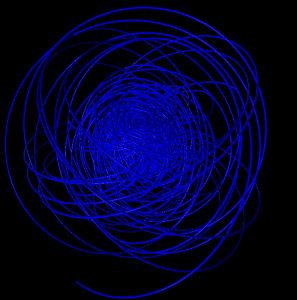
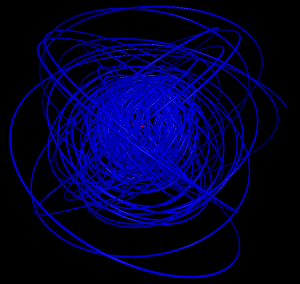
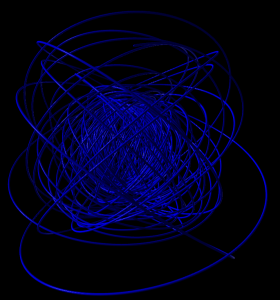
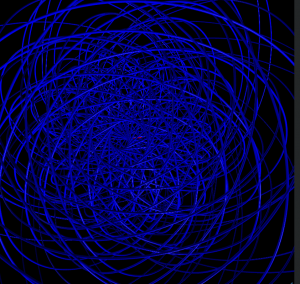
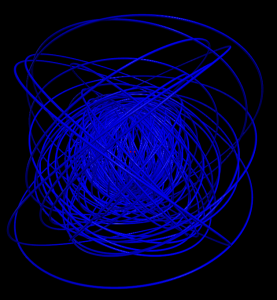
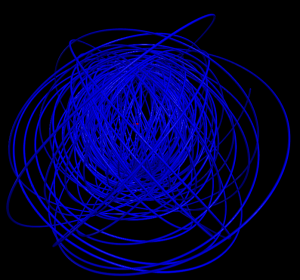
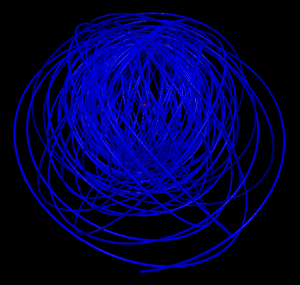
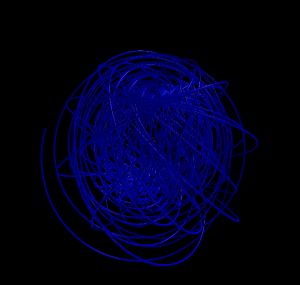
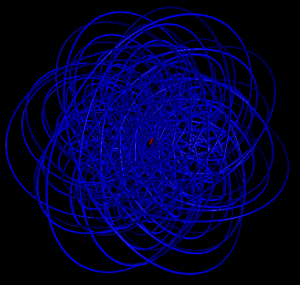
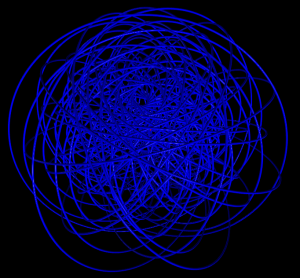
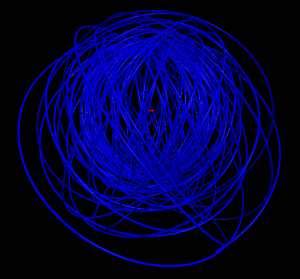
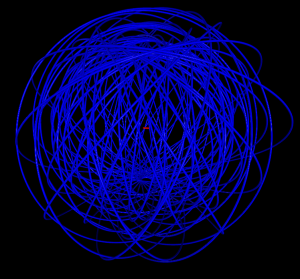
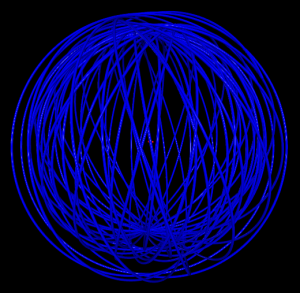
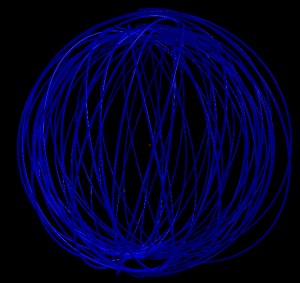
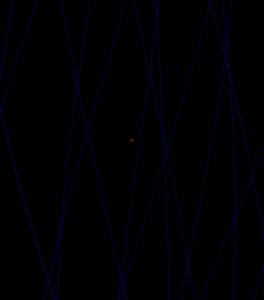
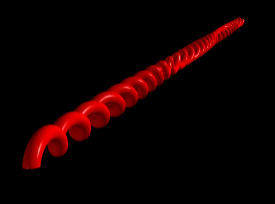
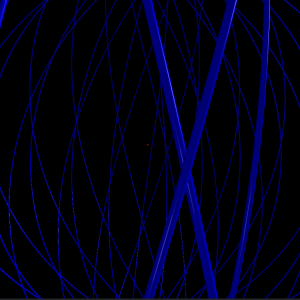
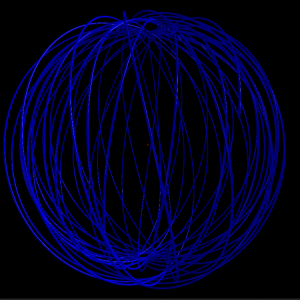
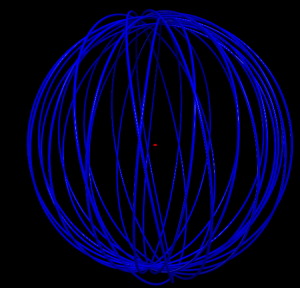
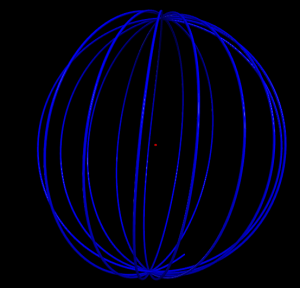
5 shells
4 shells
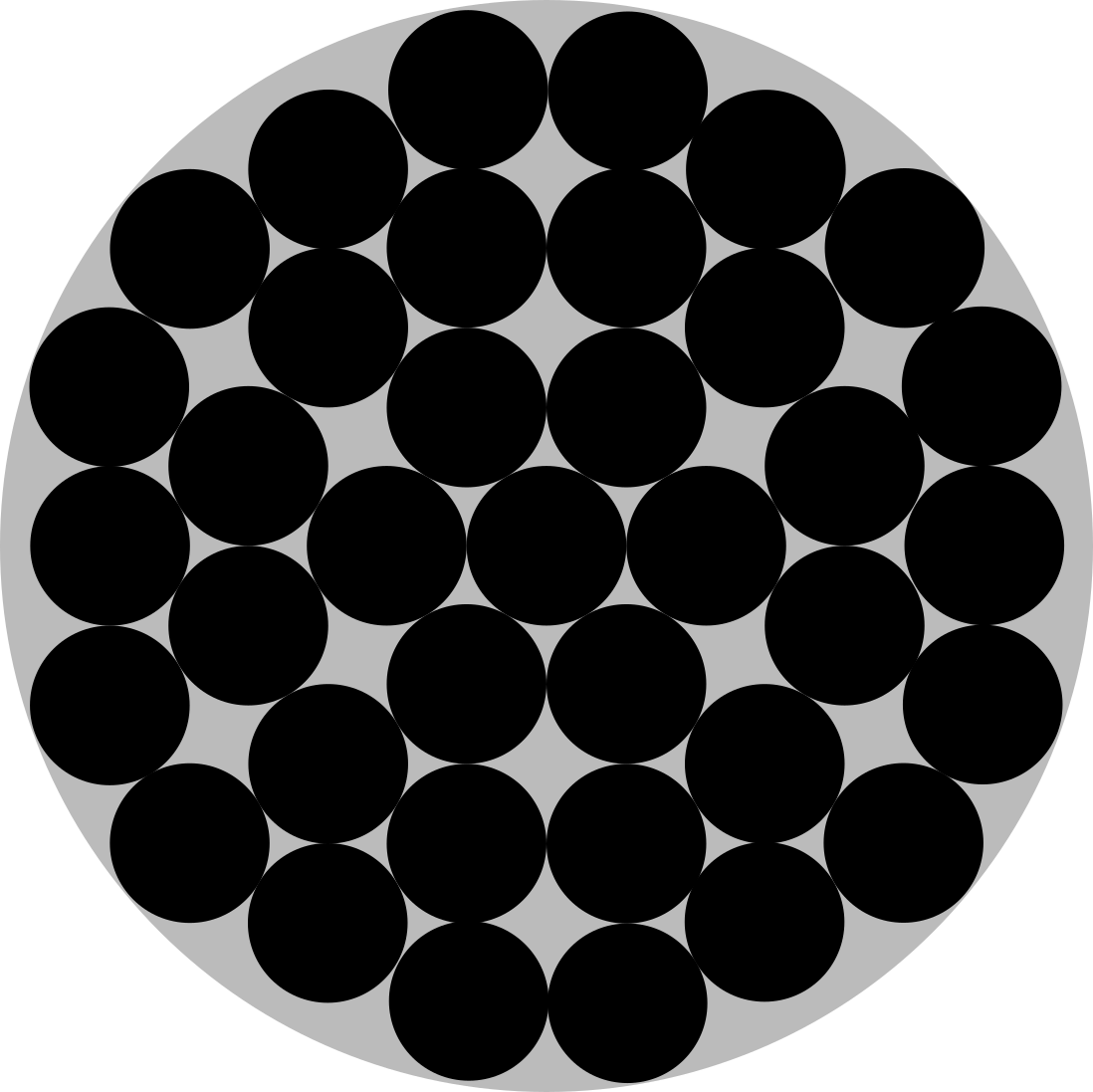
Conjecture: Densest Packing of 37 Congruent Circles in a Circle
Maybe not quite, but close:
http://hydra.nat.uni-magdeburg.de/packing/cci/cci37.html
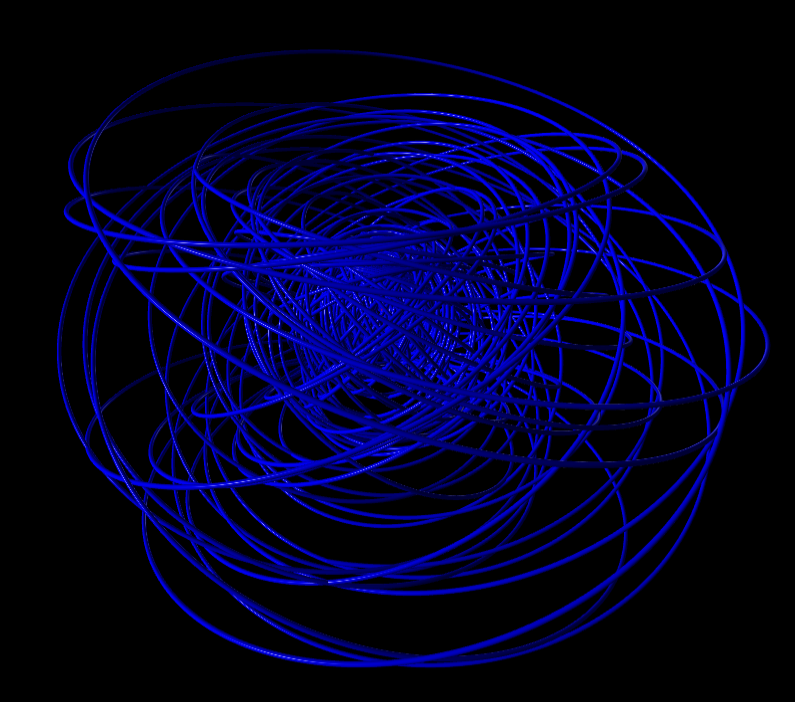
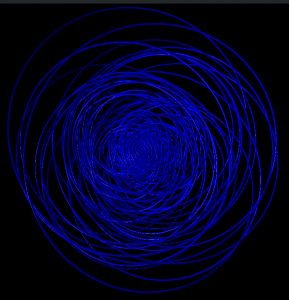
Hydrogen in a constant magnetic field
from vpython import *
scene.fullscreen = True
G = 10 # Coulomb constant in analogy to gravitational constant
# edit initial conditions here
##########
spheres = [
sphere(pos=vector(0,0,0),radius =6,color=color.red,charge=1000,mass=7200,velocity=vector(0,0,0),a = vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.red)),
sphere(pos=vector(0,100,-1),radius=2,color=color.blue,charge=-1,mass=1,velocity=vector(10,0,0),a=vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.blue)),
#sphere(pos=vector(0,12,0),radius=.08,color=color.green,mass=sqrt(4),velocity=vector(1.2,0,0.6),a=vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.green)),
#sphere(pos=vector(0,100,1),radius=2,color=color.white,charge=-1,mass=1,velocity=vector(-10,0,0),a=vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.white)),
#sphere(pos=vector(0,28,0),radius=.4,color=color.orange,mass=sqrt(80),velocity=vector(0.7,0,0.4),a=vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.orange)),
#sphere(pos=vector(0,32,0),radius=0.2,color=color.white,mass=-sqrt(10),velocity=vector(1.5,0,0.4),a=vector(0,0,0),trail=curve(color=color.white))
]
B=arrow(color=color.green,axis=vec(0,10,0))
def acceleration1on2(sphere2,sphere1):
r = sphere2.pos - sphere1.pos
r_mag = mag(r)
normal_r = norm(r)
g = ((G*sphere1.charge*sphere2.charge)/pow(r_mag,2))/sphere2.mass*normal_r
return g
t = 0
dt = .5 # trade-off between simulation speed and numerical accuracy
while 1:
rate(100)
for i in spheres:
i.a = vector(0,0,0)
soi = vector(0,0,0)
for j in spheres:
if i!=j:
i.a = i.a + acceleration1on2(i,j)
spheres[1].a += .001*cross(spheres[1].velocity, B.axis) # Lorentz force due to constant magnetic field
for i in spheres:
i.velocity = i.velocity + i.a *dt
i.pos = i.pos+i.velocity*dt
i.trail.append(pos=i.pos)
scene.center=vector(spheres[0].pos.x,spheres[0].pos.y,spheres[0].pos.z)
New ideas for a deterministic relativistic model of spin in accordance with the Stern-Gerlach-experiment
Stroboscopic Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
We can’t determine the position of a particle at one “moment” because it’s moving too fast.